|
DOI: 10.25136/2409-7144.2022.7.38467
EDN: MAZJKV
Received:
17-07-2022
Published:
05-08-2022
Abstract:
Social networks are used by 72% of the Russian population, government agencies are involved in digital communication through social networks to preserve information influence and establish a dialogue with society. The state of interaction between authorities and citizens in social networks is described by evolutionary stages, which differ in the intensity of interaction between authorities and users. In 2022, the list of popular social networks that are used in Russia has changed, a decision was made on mandatory registration of public authorities in social networks. The purpose of the article is to evaluate the practice of interaction of federal executive authorities in social networks. The study used quantitative and comparative methods that reveal the specifics of the interaction of federal executive authorities in social networks, the activity of official pages was evaluated using the social network analytics program. The study of official accounts showed that the authorities are at different stages of adaptation, some federal executive authorities are absent from social networks, the second group is at the stage of "registration and informing", the third group has advanced to the stage of "interaction". The reasons for the various activities of the authorities have been identified. The results can be useful in determining the policy of government agencies in social networks and developing recommendations on the organization of maintaining official accounts.
Keywords:
social network, social media, public administration, executive authority, communications, feedback, like, repost, e-government, openness
This article is automatically translated.
You can find original text of the article here.
The introduction of digital technologies and platform solutions in the field of public administration is a strategic task of the development of the state. [17] Digital technologies create conditions conducive to the establishment of cooperation between the authorities and citizens and have an impact on the internal efficiency of public administration [5, 22, 24]. Social networks are becoming an actual tool that increases the openness, transparency, accountability of administrative processes of authorities and ensures direct interaction with citizens [34]. The widespread use of social networks in everyday life and professional activities obliges public authorities to engage in communication with the population. The obligation of executive authorities and subordinate organizations to create pages in social networks and integrate them into official websites [25] confirms the desire to institutionalize the existing practice. At the same time, the authorities should take into account the changing conditions for the use of previously most popular social networks and the need to migrate to new platforms. Social networks have been an object of study since the mid-twentieth century [8], but the term "social networks" has become widespread in relation to the Internet space. Social networks are Internet applications designed to facilitate social interaction, as well as for the use, development and dissemination of information in society [30]. When defining the concept, the emphasis is on interactivity, efficiency and the multi–user nature of the social network, the content of which is filled with users, therefore, the network is a social structure consisting of interconnected groups and individuals [4]. Among the features of online social networks are an unlimited amount of information; a variety of types of content; minimal distribution costs; accessibility; interaction with a global audience [11]. Due to these advantages, social networks are becoming one of the main means of communication in society. According to Kepios, as of January 2022, 89% (129.8 million) of the total population use the Internet in Russia, while the number of social network users is equivalent to 72.7% of the total population and continues to grow [29]. The penetration of social networks into the life of society increases the number of studies that focus on the use of social networks in the public sector. One of the first monographs in Russia, in which social networks were studied from the point of view of management, belongs to D. A. Gubanov, D. A. Novikov, A. G. Chkhartishvili [8]. In many works, the emphasis is on political communication on social media platforms, the prospects of participating management are considered [3], political activism [1], the study is conducted from the point of view of the openness of power [10, 13, 15, 23]. According to A. N. Raskhodchikov [18], the authorities do not take into account the increasing need of the population for interactive interaction with the authorities, which hinders joint management. In the work of N. S. Zimova, E. V. Fomin, A. A. Smagina, it is indicated that social networks allow evaluating the effectiveness of government activities, the high potential of social networks as a tool of interaction is noted [12]. L. M. Belenkova, S. Yu. Belokonev justify the use of social networks to form the image of state bodies [2]. Within the framework of our research, an article by N. E. Dmitrieva [9] is of particular interest, in which official accounts of federal agencies were monitored for the first time. In the works of V.V. Zotov, A.V. Gubanov, the potential of social networks in public administration is considered [7, 35]. We also note the report "Openness of the state in Russia - 2021" [16], which includes information on the use of social networks, but does not reflect the circumstances that changed in 2022. Among the foreign authors we will mention the works of I. Mergel [31, 32, 33, 34], which largely determine the direction of research on social networks in the public sector, including the proposed structure for measuring interaction with social networks, as well as X's articles. Ignacio Criado, H. Villarde [28], R. Zumofen, V. Mabillard, M. Pasquier [36]. Currently, social media are becoming objects and means of "information management, an arena of information confrontation and an instrument of information influence in order to manipulate individuals, social groups and society as a whole" [8]. Users of social networks agree that digital content contributes to the formation of attitudes: 63% of respondents reported that social networks influence political decision-making; 58% of respondents indicate that the formation of socio-political views is influenced by networks, in addition, the majority (79%) believe that social media can distract people from really important problems and spread misinformation and intolerance (64%) [1]. The above suggests that in order to ensure the legitimacy and strengthen the existing order, the state is interested in the development of interactive communication platforms. Since December 2022, the authorities, in addition to creating an official website, are required to maintain official pages on social networks and post up-to-date information about their activities on them [25]. The adaptation of state bodies to new ways of interaction is necessary, firstly, to control the information space [15] and secondly, to build a permanent constructive dialogue with the population [6]. There is a request from the society for interaction with the authorities, according to citizens, the government should have certain characteristics, among which are [1]: – availability (openness) of information about the activities of the authorities (49%) – possibility of personal communication with government representatives (40%) – willingness of government representatives to discuss with the opposition and civil society (29%). A. N. Razkhodchikov [18] calls the communication gap an obstacle to building a dialogue between the government and society, due to the fact that the activities of the authorities do not correspond to the speed and scale of the development of Internet technologies by citizens. Indeed, in the process of joining public authorities to social networks, there are several stages [33, 36]: 1) dissemination of information (there is an account and posts are published); 2) interaction (users reacted, shared or commented on the publication on the page); 3) transaction (full-fledged cooperation).
In the first phase, the authorities consider social networks as additional channels for bringing official information to ensure the widest possible audience coverage, communication is unidirectional. At the interaction phase, communication becomes interactive, the authorities initiate receiving information and comments from users. At the third stage, the authorities, together with citizens, create plans, policies or content. Another approach suggests considering four levels of interaction between executive authorities and the population [21]: 1) the level of information; 2) the level of counseling; 3) the level of partnership; 4) the level of civil administration. The last two levels are correlated with the third stage discussed above, when citizens are involved as experts and project participants. Both approaches are comparable to the stages of the evolution of e–government ("digital presence" - simple web interaction – online transaction services - joint management) [27]. Thus, social networks directly affect the behavior of citizens outside the Internet, there is a demand for openness of government among citizens, public authorities need to adapt to new communication technologies and engage in digital communication through social networks in order to maintain information influence and establish a dialogue with society. The state of interaction between authorities and citizens in social networks is described by certain evolving stages, which differ in the intensity of interaction between authorities and users [36]. The purpose of the article is to evaluate the practice of interaction of federal executive authorities (hereinafter FOIV) in social networks. Research objectives: 1) determine the number of official accounts and the number of subscribers on the official pages of the FOIV, which will allow you to get an idea of the presence of the FOIV in social networks before making a decision on mandatory registration of official pages; 2) evaluate the activity of accounts and user involvement in communication on the official pages of the FOIV. Methods of information collection and analysis The paper considered the official accounts of federal executive authorities. The list includes the bodies listed on the website of the Government of Russia in the section "Ministries and Departments" (http://government.ru/ministries ). The official accounts of the FOIV have been identified in the following social networks: "VKontakte", "Odnoklassniki", "Telegram", "RuTube", "YouTube", "Yandex Zen", "Likee", "Tiktok". To collect information, open data from the official websites of the FOIV and social networks were used. The search for official accounts in social networks was carried out through the official websites of the FIS, which the authorities are obliged to create on the basis of Federal Law No. 8-FZ of 09.02.2009 "On providing access to information on the activities of state bodies and local self-government bodies". Most of the FOI websites contain logos of social media platforms on the main page or in the "Contacts" section. Please note that the section of the website "Government pages in social networks" does not fully reflect the list of social network accounts of the FOIV. Based on the information received, a quantitative analysis of the official pages of the FOIV in social networks (number of accounts, number of subscribers) was carried out. Information about the status of accounts is displayed as of July 1-2, 2022. The data has been studied for 70 FOI. The interactivity and the level of user engagement were assessed using absolute and average indicators related to the activity of the account and subscribers (posts; reposts; likes; comments) on the VKontakte pages. The data were summarized for a month (June 1-30, 2022) using the social network analytics program Popster.ru . As a result, information was obtained on the registration and activity of the FOIV in social networks, which allows us to determine the stage of interaction of the body with citizens. Results and discussion According to the regional report on the state of the Russian digital industry at the beginning of 2022, WhatsApp, VKontakte and Instagram, Telegram, TikTok and Odnoklassniki (from 45 to 81% of Internet users) had the largest monthly audience in Russia [29]. Facebook Instagram, Twitter, and social networks have been officially restricted in Russia since March 2022, so the updating of information on these social networks by public authorities has been discontinued and these networks have not been considered by us. According to VTSIOM, in April 2022, the top 5 most popular social networks and messengers among Russians included WhatsApp (87%), YouTube (75%), VKontakte (62%), Telegram (55%) and Odnoklassniki (42%), Instagram Facebook's audience has almost halved, and Telegram has become the fastest growing messenger [20]. At the time of preparation of the article, the FOIV had registered accounts in social networks: "VKontakte", "Odnoklassniki", "Telegram", "RuTube", "YouTube", "Yandex Zen", "Likee", "Tiktok". Out of 70 FOIVS have a page in at least one of the social networks – 59 (84%). The Ministry of Emergency Situations of Russia demonstrates a great openness to social networks, the agency has official accounts in all eight of the above-mentioned networks. 11 bodies (the SVR of Russia, the FSB of Russia, the Main Directorate of Special Programs of the President of the Russian Federation, the Office of the President of the Russian Federation, the FSO of the Russian Federation, the FSVTS, the FSTEC of Russia, the SFS of the Russian Federation, the Federal Assay Chamber, Roszheldor and Rosmorrechflot) do not have a single page on social networks.
The main part of the FOI is registered in more than one network (93%). Most of the FOIV have accounts in VKontakte – 56 accounts (in 2019 – 29), the second most popular Telegram platform – 53 accounts, 41 accounts – in the Odnoklassniki network, 34 FOIV opened a channel in RuTube, 10 – registered in Yandex Zen, 3 FOIV – in "Tiktok" (Figure 1). 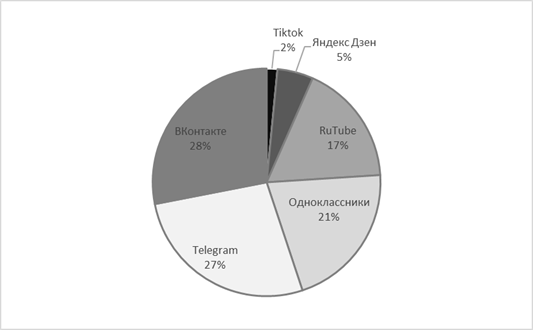
Fig. 1.The official pages of the FOIV in social networks The changes correspond to the recommendations given by ANO Dialog, it is mandatory to use VKontakte and Telegram for work, Odnoklassniki is optional. Note that the blocking of social networks completely changed the composition of the official accounts of the FOIV, so in 2019 the most popular network was Twitter (46 FOIV out of 56 owned the official page), followed by Facebook – 44, VKontakte had 29 accounts (third place), and the Odnoklassniki network remained the least in demand, there are 11 accounts in total [19]. "Telegram" in 2019 was not considered by the FOIV as a possible channel of official communication. A comparison by the number of accounts is shown in Figure 2. The total number of accounts has increased (2019 – 182, 2022 – 216). 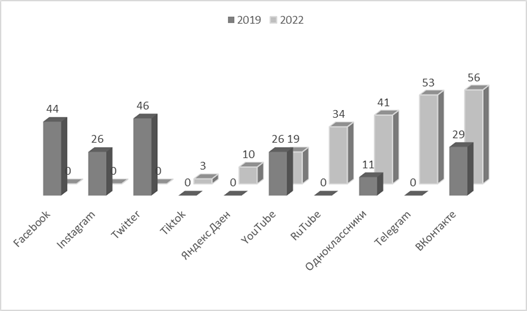
Fig. 2 Comparison of the number of official FOIV accounts in 2019 and 2022 x A registered account does not mean its full use for informing and direct interaction with citizens. A page or group on a social network is primarily evaluated by the number of subscribers. Figure 3 shows the number of users registered on the official pages of the FOI in 2022 across the three leading networks. 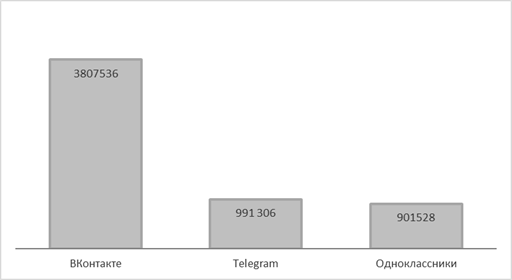
Fig. 3 The number of subscribers of the FOIV accounts in 2022 (people) Let's add that previously the number of subscribers on YouTube was significant, for example, the channel of the Russian Ministry of Defense had more than a million (1.07 million) subscribers, but currently the update has been discontinued. The data show that the audience is increasing, the largest number of subscribers at the pages of the FOIV in the VKontakte network (2019 – 1947618, 2022 – 3807536 subscribers on all official accounts of the FOIV), followed by Telegram and (Odnoklassniki 2019 – 578654; 2022 – 901528). Figure 4 shows an increase in the number of registered users on the most popular Facebook pages on the VKontakte network in comparison with 2019. 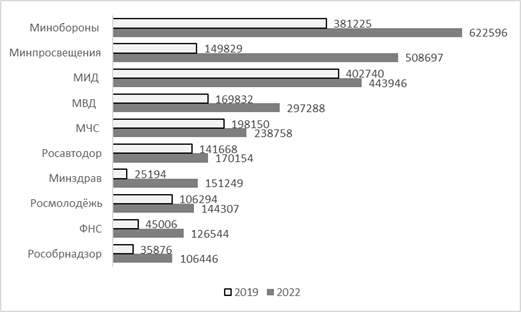 Fig. 4 Increase in the number of registered users of the official accounts of the FOIV in "In Contact" (people) Let's briefly summarize the results obtained for the first task of the study – at the stage of "registration and informing" of the process of joining public authorities to social networks, 59 (84%) of the 70 FOIS are located, the registration of FOIS in more than one network becomes the norm (93%). Mostly FOIV have accounts in VKontakte (95%), followed by Telegram and Odnoklassniki. Despite the rejection of the most popular networks earlier, the total number of accounts has increased, a significant increase in the audience is shown by the pages of the FOIV on the VKontakte network, the number of subscribers of the official accounts of the FOIV VKontakte exceeds the number of subscribers on other platforms. Of course, high-quality work with citizens requires not only a review of quantitative indicators, but also an analysis of the target audiences of the FOIV pages. It should be noted that online registration is the first phase of the FOIV adaptation to interaction in a social network. Connection does not mean regular use of new opportunities in the daily activities of the FOIV, just as a formal increase in subscribers does not mean active communication. Moving to the next stage of "interaction" means that the FOIV is ready for dialogue and moves from "unidirectional information to effective communication on specific problems", shows a desire to listen to the opinions and arguments of users [9]. In a social network, feedback is expressed in setting likes/dislikes, commenting on publications or republishing a message (repost) [35]. Next, let's consider the intensity of interactive communication of the FOIV in the VKontakte network. Let's start with the most important indicator that reflects the interaction between representatives of the authority and citizens in social networks – publication activity [35]. According to the total number of posts, the FOI differ significantly, since the Rosstat service published 12 posts during the period under review (the lowest indicator), Rosaccreditation prepared 551 posts (an average of 18 posts per day), the rest of the bodies occupy an intermediate position. It is difficult to establish the optimal level of the average daily and average monthly number of publications for executive authorities [35], therefore each body independently determines the number of posts, in our case the median is 54 posts per month.
A high frequency of publications does not necessarily have a positive effect on user interest. The leader in the number of posts of Rosaccreditation on 551 posts, readers left 1 comment, 253 likes. For comparison, the Ministry of Defense published 470 posts that received 44,386 comments and more than 1 million likes. The "like" function is designed to express the attitude of users to a particular content. Likes indicate the attractiveness of the publication for users, the number of likes is considered as support and a positive assessment of the proposed message. Figure 5 shows data on the average number of likes on the posts of the FOIV for the period under review, the rest scored less than 100 likes. 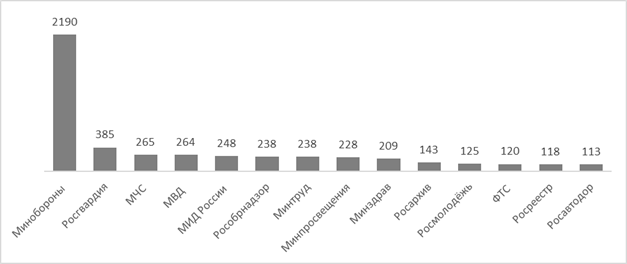
Fig. 5 The number of likes on average (official pages of the FOIV VKontakte, June 1-30, 2022) Another metric that allows, on the one hand, to assess the involvement of users, and on the other hand, the relevance and quality of content is re–publication (repost). Figure 6 shows the average number of reposts on the official pages of the FOIV. 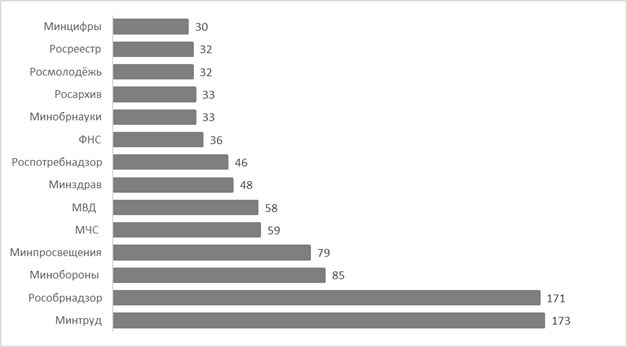
Fig. 6. The number of reposts on average (official pages of the FOIV VKontakte, June 1-30, 2022) The number of likes and reposts show the interest of users in the information, expand the audience of the account. In our opinion, the republication of content and the expression of approval by likes are "passive" ways of expressing an opinion. An indicator of engagement and readiness for dialogue is the discussion of publications by users and answers to questions. The possibility of commenting is open on the pages of most of the accounts of FOIV, but 20% of the pages (12 out of 56) have comments completely disabled. The results of the number of comments on average are shown in Figure 7. A total of 27 FOIVS are presented, there is virtually no activity in the form of discussion of published information on the pages of FOIVS that are not specified. 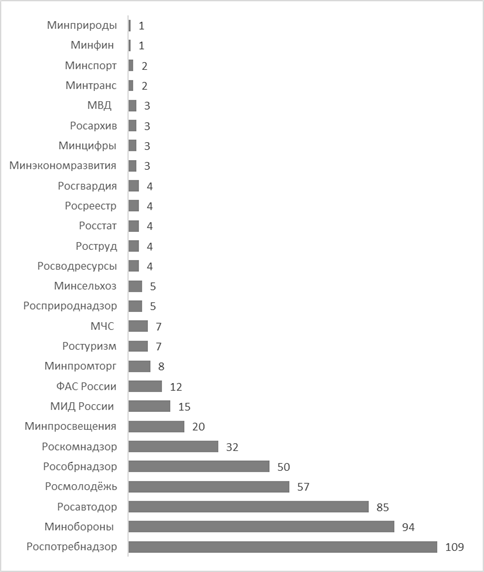
Fig. 7 The average number of comments (official pages of the FOIV VKontakte, June 1-30, 2022) We agree that "functionally, any comment is an expression of a personal attitude to the surrounding reality, that is, an expression of one's own assessment of the elements of the world picture" [14], and the authority is focused on satisfying public interest, therefore tracking all opinions is costly and leads to information overload. "The selection and interpretation of relevant and representative signals from the mass of online interactions is a real problem" [26], therefore, comments on posted publications are limited for users on some pages of the FOIV. The adoption of new requirements for information work obliges the authorities from December 2022 to work with citizens' questions and maintain feedback. Let's assume that "the passive strategy of listening and absorbing comments, which gives valuable information from the audience" [33], will be replaced by active interaction. The question arises about the reasons for the different activity of the FOIV in the use of social networks. It is important to take into account that FOIV perform various functions in the state, for example, the goals and objectives of the Ministry of Education of Russia differ significantly from the control and supervisory activities of Rostechnadzor, therefore, the use of innovative communication tools should take into account the specifics of the organization and not turn into a formal goal. We emphasize that the regulatory regulation in the field of openness is common to FOIV, but the authorities independently develop openness strategies, including ways to build a dialogue with citizens. The changes that are included in the new edition of the law "On Information, Information Technologies and Information Protection" require the expansion of ways to ensure access to information and create an obligation for authorities to use official pages on social networks to interact with citizens [25]. Most of the departments that did not have an account are directly subordinate to the President of the Russian Federation, these bodies are given the right, but not the obligation, to create official pages for posting information about their activities on the Internet. It should be noted that the activities of the SVR of Russia, the FSB of Russia, the FSO of Russia involve the use of restricted access information and a special mode of interaction with citizens, in this case openness should not violate security. The Main Directorate of Special Programs of the President of the Russian Federation, the Office of the President of the Russian Federation, the SFS of Russia, the Federal Service for Military-Technical Cooperation perform special functions. The absence of accounts of the FSTEC of Russia, the Federal Assay Chamber, Roszheldor and Rosmorrechflot agencies in social networks is more difficult to justify, since these bodies provide public services, therefore they must have various channels of communication with citizens and organizations.
Possible obstacles hindering the introduction of social networks in the public sector were summarized in the work of X. Criado, H.Villodre [28]. They pointed out the following barriers: organizational culture; lack of resources for maintenance, monitoring and evaluation; security; lack of a management structure; digital illiteracy; legal problems; potential abuse by government officials; lack of control over suppliers; lack of political support; data and content management problems; lack of economic benefits. A.V. Gubanov believes that the use of networks depends on the differentiation of departmental competence; the representation of the target category in the network; the competence of specialists [7]. Our assumption is that the differences primarily depend on the communication policy and practice in a particular authority. Readiness for interactive interaction is influenced by the manager's preferred way of working with information and general openness to innovation in communications. The obstacle to maintaining a page is a lack of resources, account maintenance requires time and trained personnel who are able to provide management of the appropriate types of communication. There is a lack of analytical support, benefit analysis or success indicators regarding the use of social networks in government, although some researchers note an increase in management efficiency [12]. The lack of clear guidelines creates complex ethical and legal dilemmas in the process of maintaining the official pages of the authority [33]. Thus, the executive authorities are adapting to new ways of interacting with citizens in social networks. Prior to the adoption of the law obliging the authorities to maintain official pages on social networks, most of the FOI had registered on several social media platforms. Under the influence of political factors, there have been significant changes in the composition of the social networks used, the total number of accounts has increased. The VKontakte social network has taken the leading positions in terms of the number of accounts and the number of subscribers to the official pages of the FOIV, followed by Telegram and Odnoklassniki, in 2019 the most popular networks are Twitter, Facebook, VKontakte. The activity of accounts and the involvement of users on the pages of the FOIV varies, most of the FOIV have moved from the "registration and informing" stage to the "interaction" stage, which is characterized by interactive communication and manifests itself in the expression of attitude to publications (likes), secondary publication of relevant materials (reposts) and commenting on publications. Further development involves the transition to the stage of "partnership and joint management" and requires qualitative research. The obligation for public authorities to create official pages on social media platforms will speed up the process of two-way communication.
References
|
1.
|
Barash, R. E. Social media as a factor in the formation of socio-political attitudes, the Russian context // Monitoring of public opinion: economic and social changes. - 2022. – No. 2. – pp. 430-453.
|
|
2.
|
Belenkova, L. M. Social networks in information policy: formation of the image of public authorities / L. M. Belenkova, S. Yu. Belokonev // Citizen. Elections. Power. – 2020. – No. 1. – pp. 92-102.
|
|
3.
|
Vasilenko, L. A. Using the potential of social media in the formation of participating management / L. A. Vasilenko, V. V. Zotov, S. A. Zakharova // Bulletin of the Peoples' Friendship University of Russia. Series: Sociology. - 2020. – Vol. 20. – No. 4. – pp. 864-876.
|
|
4.
|
Influence through social networks: under the general editorship of E.G. Alekseeva. – M.: FOCUS-MEDIA Foundation, 2010. – p.29.
|
|
5.
|
Grigoriev, A.V. Implementation of the constitutional right of citizens to manage state affairs in conditions of digitalization / A.V. Grigoriev // Journal of Russian Law. – 2020. – No. 2. – pp. 45-57.
|
|
6.
|
Gromova, T. N. State communication: theoretical model and regional practice / T. N. Gromova // Bulletin of the Russian Communication Association. - 2002. – No. 1. – pp. 43-52.
|
|
7.
|
Gubanov, A.V. Assessment of capitalization of official accounts of regional government bodies in social media / A.V. Gubanov // Communicologiya. – 2019. – Vol. 7. – No. 4. – pp. 71-81.
|
|
8.
|
Gubanov, D. A. Social networks: models of information influence, management and confrontation / D. A. Gubanov, D. A. Novikov, A. G. Chkhartishvili. – Moscow, 2010. – p.4.
|
|
9.
|
Dmitrieva, N. E. For communication in the network: results of monitoring the openness of federal executive authorities in social networks // Issues of state and municipal administration. - 2015. – No. 2. – C. 123-146.
|
|
10.
|
Ermolaev, V. P. Vkontakte social network as a modern channel of political communication / V. P. Ermolaev // Information Wars. – 2017. – No. 3. – pp. 47-55.
|
|
11.
|
Efimova, G. Z. Professional promotion of higher school teachers in virtual social networks // Monitoring of public opinion: economic and social changes. – 2022. – No. 2. – pp. 317-341.
|
|
12.
|
Zimova, N. S. Social networks as a new channel of interaction between society and government / N. S. Zimova, E. V. Fomin, A. A. Smagina // Scientific result. Sociology and Management. – 2020. – Vol. 6. – No. 2. – pp. 159-171.
|
|
13.
|
Kaminchenko, D. I. Political functions of Instagram at the regional level / D. I. Kaminchenko // Information Society. – 2022. – No. 2. – pp. 76-84.
|
|
14.
|
Karpoyan, S. M. Commentary functions on various communicative platforms of social networks / S. M. Karpoyan // Humanities, socio-economic and social sciences. - 2015. – No. 11-2. – pp. 242-245.
|
|
15.
|
Kryshtanovskaya, O. V., Filippova, A. Studies of political communication: the state and social networks // Bulletin of the GUU. – 2018. – No. 6. – pp.171-176.
|
|
16.
|
Openness of the State in Russia – 2021 / TSPUR; Information Culture; Accounting Chamber. – Moscow, 2021. – 145 p.
|
|
17.
|
Passport of the federal project Digital Public Administration (approved by the Presidium of the Government Commission on Digital Development, the Use of Information Technologies to improve the quality of life and business conditions (Protocol No. 9 dated May 28, 2019) URL: https://base .garant.ru/72302270 / (accessed: 10.07.2022).
|
|
18.
|
Raskhodchikov, A. N. Information and communication interaction between government and society: in search of effective technologies / A. N. Raskhodchikov // Monitoring of public opinion: economic and social changes. – 2017. – No. 2. – pp. 263-273.
|
|
19.
|
Roslyakova, M. V. Social networks in the professional activity of civil servants: Russian practice and foreign experience / M. V. Roslyakova // Sociodynamics. – 2019. – No. 9. – pp. 82-99.
|
|
20.
|
The Russian audience of social networks and messengers: changes against the background of a special operation // VTSIOM: ofits. website URL: https://wciom.ru/analytical-reviews/analiticheskii-obzor/rossiiskaja-auditorija-socialnykh-setei-i-messendzherov-izmenenija-na-fone-specoperacii (access date: 04.07.2022)
|
|
21.
|
Smolina, E. G. Levels and forms of interaction between executive authorities and the population in the Internet space (on the example of Volgograd) // Colloquium-journal. – 2020. – No. 2. – pp. 13-14.
|
|
22.
|
Smorgunov, L. V. Digitalization and network efficiency of state manageability / L. V. Smorgunov // Political science. - 2021. – No. 3. – pp. 13-36.
|
|
23.
|
Startsev, A. A., Grishanin, N. V. Social networks in the process of communication between government and society // Communicology. – 2018. – No. 5. – pp.108-119.
|
|
24.
|
Sungurov, A. Yu. On electronic and traditional public participation in modern public policy / A. Yu. Sungurov, D. A. Arkatov // Political Science. – 2021. – No. 3. – pp. 54-71.
|
|
25.
|
Federal Law No. 270-FZ of 14.07.2022 "On Amendments to the Federal Law "On Ensuring Access to Information on the Activities of State Bodies and Local Self-Government Bodies" and Article 10 of the Federal Law "On Ensuring Access to Information on the Activities of Courts in the Russian Federation"" URL: http://publication.pravo.gov.ru/Document/View/0001202207140024 (accessed: 07/14/2022).
|
|
26.
|
Bekkers, V., et al., (2013). Social media monitoring: Responsive governance in the shadow of control? Government Information Quarterly (30): 335-342
|
|
27.
|
Chun, Soon & Shulman, Stuart & Sandoval Almazan, Rodrigo & Hovy, Eduard. (2010). Government 2.0: Making Connections Between Citizens, Data and Government. Information Polity. 15 (1-2). 1-9. 10.3233/IP-2010-0205.
|
|
28.
|
Criado, J. I., & Villodre, J. (2022). Revisiting social media institutionalization in government. An empirical analysis of barriers. Government information quarterly, 39(2), 101643.
|
|
29.
|
Digital 2022: The Russian Federation URL: https://datareportal.com/reports/digital-2022-russian-federation (дата обращения: 10.07.2022).
|
|
30.
|
Kavanaugh, A. L., Fox, E. A., Sheetz, S. D., Yang, S., Li, L. T., Shoemaker, D. J., ... & Xie, L. (2012). Social media use by government: From the routine to the critical. Government Information Quarterly, 29(4), 480-491.
|
|
31.
|
Mergel, I. (2016). Social media institutionalization in the US federal government. Government information quarterly, 33(1), 142-148.
|
|
32.
|
Mergel, I., & Bretschneider, S. I. (2013). A three‐stage adoption process for social media use in government. Public administration review, 73(3), 390-400.
|
|
33.
|
Mergel, I. (2013). A framework for interpreting social media interactions in the public sector. Government information quarterly, 30 (4), 327-334.
|
|
34.
|
Mergel, I. (2013). Social media adoption and resulting tactics in the US federal government. Government information quarterly, 30(2), 123-130.
|
|
35.
|
Zotov, V. V., & Gubanov, A. V. (2021). Interaction between public authorities and stakeholders in social media (comparative analysis of the regional practician). KnE Social Sciences, 315-322.
|
|
36.
|
Zumofen, R., Mabillard, V., Pasquier, M. (2022). Social media use in Central and Eastern European cities: Defining government-citizen relationships through phases. NISPAcee 30th Annual Conference / Bucharest, Romania (2-4 June 2022).
|
Peer Review
Peer reviewers' evaluations remain confidential and are not disclosed to the public. Only external reviews, authorized for publication by the article's author(s), are made public. Typically, these final reviews are conducted after the manuscript's revision. Adhering to our double-blind review policy, the reviewer's identity is kept confidential.
The list of publisher reviewers can be found here.
In the peer–reviewed article "Social networks in the activities of executive authorities: adaptation to new ways of interaction", the subject of the study is social networks as an Internet application in which social interaction between federal authorities and the population unfolds. The purpose of this work is to evaluate the practice of interaction of federal executive authorities in social networks. The research methodology is based on the analysis of publications on the issues of social and network interaction between public administration bodies and the population. The work is based on the analysis of the official accounts of federal executive authorities from the list of the section "Ministries and departments" of the Russian Government website in the following social networks: VKontakte, Odnoklassniki, Telegram, RuTube, YouTube, Yandex Zen, Likee, Tiktok. To collect information, open data from the official websites of the FOIV and social networks were used. The data was summarized for the month (June 1-30, 2022) using the social network analytics program Popster.ru . This makes the analysis sufficiently objective and comprehensive. The relevance of the research is determined by the fact that digital technologies create conditions for cooperation between government and citizens and have an impact on the effectiveness of public administration. Social networks are becoming an actual tool that increases the transparency of authorities and ensures direct interaction with citizens. The need to control the information space and build a constant constructive dialogue with the population actualizes the problem of adapting government agencies to new ways of interaction. The scientific novelty of the work is related to the empirical substantiation of the claim that executive authorities are adapting to new ways of interacting with citizens on social networks. The authors state that under the influence of political factors, there have been significant changes in the composition of social networks used by federal executive authorities, and the total number of accounts has increased. The VKontakte social network has taken the leading position in terms of the number of accounts and the number of subscribers to the official pages. Noteworthy is the conclusion about the transition from the "registration and information" stage to the "interaction" stage, which is characterized by interactive communication and manifests itself in expressing attitudes towards publications (likes), secondary publication of relevant materials (reposts) and commenting on publications. This study is characterized by general consistency, literacy of presentation, clarity and empirical verification of conclusions. The reviewed work is characterized by the logical presentation of the material, has novelty and depth of elaboration of the material. The bibliography of the work includes 39 sources on the problems of social network interaction between public administration bodies and the population. As a result, the appeal to the main opponents is duly present. However, when making a list of references, the author does not use the recommended GOST. In particular, it is impractical, if there is a printed publication, to indicate its address on the Internet, especially since the latter are sites (sciencedirect, researchgate, etc.) that provide access to scientific publications (but not by the publishers themselves). The work will be of interest to state and municipal employees, scientists dealing with the problems of social networking between public administration bodies and the population. The article "Social networks in the activities of executive authorities: adaptation to new ways of interaction" has scientific and practical significance. The work can be published after eliminating the comments on the design of the list of references.
|


















 Статья опубликована с лицензией Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0) – Лицензия «С указанием авторства – Некоммерческая».
Статья опубликована с лицензией Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0) – Лицензия «С указанием авторства – Некоммерческая».
 Рус
Рус



